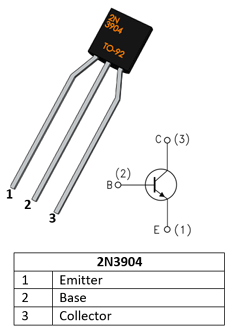
2N3904 NPN n-type, General Purpose Transistors (max. 200mA) - TO-92
-
RM0.40
- Product Code: 2N3904
- Availability: In Stock
2N3904 is a NPN transistor hence the collector and emitter will be left open (Reverse biased) when the base pin is held at ground and will be closed (Forward biased) when a signal is provided to base pin. 2N3904 has a gain value of 300; this value determines the amplification capacity of the transistor. The maximum amount of current that could flow through the Collector pin is 200mA, hence we cannot connect loads that consume more than 200mA using this transistor. To bias a transistor we have to supply current to base pin, this current (IB) should be limited to 5mA.
When this transistor is fully biased then it can allow a maximum of 200mA to flow across the collector and emitter. This stage is called Saturation Region and the typical voltage allowed across the Collector-Emitter (VCE) or Collector-Base (VCB) could be 40V and 60V respectively. When base current is removed the transistor becomes fully off, this stage is called as the Cut-off Region and the Base Emitter voltage could be around 600 mV.
Features
Package Content
When a transistor is used as a switch it is operated in the Saturation and Cut-Off Region as explained above. As discussed a transistor will act as an Open switch during Forward Bias and as a closed switch during Reverse Bias, this biasing can be achieved by supplying the required amount of current to the base pin. As mentioned the biasing current should maximum of 5mA. Anything more than 5mA will kill the Transistor; hence a resistor is always added in series with base pin. The value of this resistor (RB) can be calculated using below formulae.
RB = VBE / IB
Where, the value of VBE should be 5V for 2N3904 and the Base current (IB depends on the Collector current (IC). The value of IB should not exceed mA.
A Transistors acts as an Amplifier when operating in Active Region. It can amplify power, voltage and current at different configurations.
Some of the configurations used in amplifier circuits are
- Common emitter amplifier
- Common collector amplifier
- Common base amplifier
Of the above types common emitter type is the popular and mostly used configuration. When uses as an Amplifier the DC current gain of the Transistor can be calculated by using the below formulae
DC Current Gain = Collector Current (IC) / Base Current (IB)
How to Safely Long Run in a Circuit:
To get good and long term performance from this transistor it is suggested to not drive loads more than 100mA, always use a suitable base resistor, do not provide collector-emitter voltage more than 40V and always operate or store in temperatures above -55 centigrade and below +150 centigrade.
Tags: NPN, Amplifier Transistor, General Purpose