Omnidirectional Microphone Module I2S Interface INMP441 MEMS High Precision Low Power Ultra Small Volume I2S Interface for ESP32
-
RM18.00
- Product Code: INMP441
- Availability: 10-14 Days
Description:
The INMP441 is a high-performance, low power, digital-output, omnidirectional MEMS microphone with a bottom port. The INMP441 is available in a thin 4.72 x 3.76 x 1 mm surface mount package. It is reflow- solder compatible with no sensitivity degradation. The INMP441 is halide free. The INMP441 has a high signal-to-noise ratio and is an excellent choice for near field applications. The INMP441 has a flat wideband frequency response that results in high definition of natural sound.
Features:
1. Digital I2S interface with high precision 24-bit data
2. High signal to noise ratio is 61 dBA
3. High sensitivity – 26 dBFS
4. Stable frequency response from 60 Hz to 15 kHz
5. Low power consumption: low current consumption 1.4 mA
6. High PSR: -75 dBFS
Package includes:
1×I2S Interface INMP441 MEMS High Precision Low Power Ultra small volume for ESP32
Interface definition:
This product provides tutorials for using ESP32 modules with I2S functionality
Connect to ESP32:
Here is how we will be hooking up our microphone module and ESP32.
Hardware requirements:
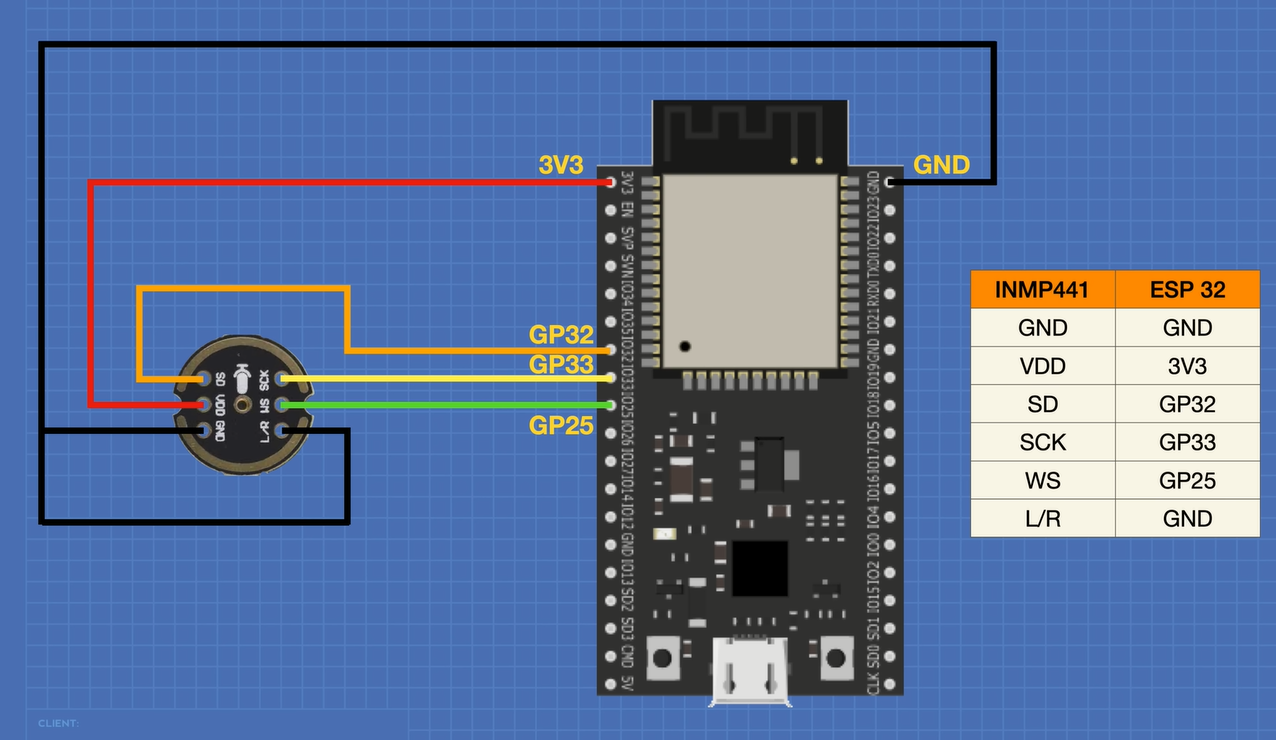
Note that your ESP32 may have a different pinout from the one illustrated here, use the GPIO numbers instead of physical pins to connect your module.
/*
ESP32 I2S Microphone Sample
esp32-i2s-mic-sample.ino
Sample sound from I2S microphone, display on Serial Plotter
Requires INMP441 I2S microphone
Faranux Electronics
*/
// Include I2S driver
#include <driver/i2s.h>
// Connections to INMP441 I2S microphone
#define I2S_WS 25
#define I2S_SD 33
#define I2S_SCK 32
// Use I2S Processor 0
#define I2S_PORT I2S_NUM_0
// Define input buffer length
#define bufferLen 64
int16_t sBuffer[bufferLen];
void i2s_install() {
// Set up I2S Processor configuration
const i2s_config_t i2s_config = {
.mode = i2s_mode_t(I2S_MODE_MASTER | I2S_MODE_RX),
.sample_rate = 44100,
//.sample_rate = 11025, if you like
.bits_per_sample = i2s_bits_per_sample_t(16),
.channel_format = I2S_CHANNEL_FMT_ONLY_LEFT,
//.communication_format = i2s_comm_format_t(I2S_COMM_FORMAT_STAND_I2S),
.communication_format = i2s_comm_format_t(I2S_COMM_FORMAT_I2S | I2S_COMM_FORMAT_I2S_MSB),
.intr_alloc_flags = 0,
.dma_buf_count = 8,
.dma_buf_len = bufferLen,
.use_apll = false
};
i2s_driver_install(I2S_PORT, &i2s_config, 0, NULL);
}
void i2s_setpin() {
// Set I2S pin configuration
const i2s_pin_config_t pin_config = {
.bck_io_num = I2S_SCK,
.ws_io_num = I2S_WS,
.data_out_num = -1,
.data_in_num = I2S_SD
};
i2s_set_pin(I2S_PORT, &pin_config);
}
void setup() {
// Set up Serial Monitor
Serial.begin(115200);
Serial.println(" ");
delay(1000);
// Set up I2S
i2s_install();
i2s_setpin();
i2s_start(I2S_PORT);
delay(500);
}
void loop() {
// False print statements to "lock range" on serial plotter display
// Change rangelimit value to adjust "sensitivity"
int rangelimit = 3000;
Serial.print(rangelimit * -1);
Serial.print(" ");
Serial.print(rangelimit);
Serial.print(" ");
// Get I2S data and place in data buffer
size_t bytesIn = 0;
esp_err_t result = i2s_read(I2S_PORT, &sBuffer, bufferLen, &bytesIn, portMAX_DELAY);
if (result == ESP_OK)
{
// Read I2S data buffer
int16_t samples_read = bytesIn / 8;
if (samples_read > 0) {
float mean = 0;
for (int16_t i = 0; i < samples_read; ++i) {
mean += (sBuffer[i]);
}
// Average the data reading
mean /= samples_read;
// Print to serial plotter
Serial.println(mean);
}
}
}